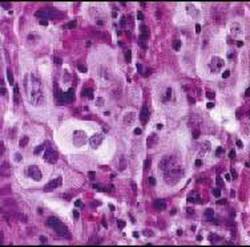
What Are the Lung Cancer Types and Their Importance?
Tumors of the lung arise from the lining of the windpipes (squamous cell cancers) or from the gland-like portions of the rest of the organ (adenocarcinomas). These are the most common specific types of lung cancer but there are others. For instance, there is a type that comes from the cells responsible for making nerves and endocrine organs. This type makes a small cell while all the other types make a large cancer cell under the microscope. For practical purposes, all lung tumors are grouped into these two categories. Here are pictures of these tumors and some important facts about them.
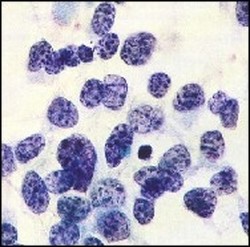 Notice that the cells are almost only blue nucleus (DNA) material making them "small" under the microscope.
Notice that the cells are almost only blue nucleus (DNA) material making them "small" under the microscope.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Facts:
Facts:
- 20% of lung cancer cases
- Usually spread to other parts of the body when discovered
- Generally treated by chemotherapy
- Usually central
- 60's age group